Lymphangitis
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
5 likes•2,730 views
Lymphangitis is inflammation of lymphatic channels due to infectious or noninfectious causes. Potential pathogens include bacteria, mycobacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Lymphangitis most commonly develops after cutaneous inoculation of microorganisms into the lymphatic vessels through a skin wound or a distal infection complication.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to Lymphangitis
Similar to Lymphangitis (20)
Lymphadenopathy / dental implant courses by Indian dental academy 

Lymphadenopathy / dental implant courses by Indian dental academy
Lymphangitis-1.pptx physiotherapy ppt general surgery

Lymphangitis-1.pptx physiotherapy ppt general surgery
urinary track infection etiology ,cystitis,acute chronic pyelonephritis

urinary track infection etiology ,cystitis,acute chronic pyelonephritis
FILARIASIS condition mainly seen on community area

FILARIASIS condition mainly seen on community area
More from Priya
More from Priya (20)
Recently uploaded
Holistic Approaches to Depression, Mental Well-Being, Mind Health, and Stress Treatment.Unlocking Holistic Wellness: Addressing Depression, Mental Well-Being, and St...

Unlocking Holistic Wellness: Addressing Depression, Mental Well-Being, and St...Health Kinesiology Natural Bioenergetics
Recently uploaded (20)
How to buy 5cladba precursor raw 5cl-adb-a raw material

How to buy 5cladba precursor raw 5cl-adb-a raw material
Storage of Blood Components- equipments, effects of improper storage, transpo...

Storage of Blood Components- equipments, effects of improper storage, transpo...
Top 15 Sexiest Pakistani Pornstars with Images & Videos

Top 15 Sexiest Pakistani Pornstars with Images & Videos
Mgr university bsc nursing adult health previous question paper with answers

Mgr university bsc nursing adult health previous question paper with answers
Hi Fi * Surat ℂall Girls Surat Dumas Road 8527049040 WhatsApp AnyTime Best Su...

Hi Fi * Surat ℂall Girls Surat Dumas Road 8527049040 WhatsApp AnyTime Best Su...
High Purity 99% PMK Ethyl Glycidate Powder CAS 28578-16-7

High Purity 99% PMK Ethyl Glycidate Powder CAS 28578-16-7
parliaments-for-health-security_RecordOfAchievement.pdf

parliaments-for-health-security_RecordOfAchievement.pdf
Hemodialysis: Chapter 1, Physiological Principles of Hemodialysis - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 1, Physiological Principles of Hemodialysis - Dr.Gawad
CONGENITAL HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS by Dr M.KARTHIK EMMANUEL

CONGENITAL HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS by Dr M.KARTHIK EMMANUEL
Tips and tricks to pass the cardiovascular station for PACES exam

Tips and tricks to pass the cardiovascular station for PACES exam
Unlocking Holistic Wellness: Addressing Depression, Mental Well-Being, and St...

Unlocking Holistic Wellness: Addressing Depression, Mental Well-Being, and St...
Lymphangitis
- 2. INTRODUCTION Lymphangitis is inflammation of lymphatic channels due to infectious or noninfectious causes. Potential pathogens include bacteria, mycobacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Lymphangitis most commonly develops after cutaneous inoculation of microorganisms into the lymphatic vessels through a skin wound or as a complication of a distal infection. The pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, microbiology, diagnosis, and treatment of lymphangitis will be reviewed here. Further information about the individual etiologies of lymphangitis is discussed in detail separately.
- 3. Lymphangitis is an infection of the lymph vessels (channels). It is a complication of some bacterial infections.
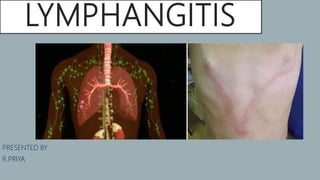
- 4. ANATOMY OF LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
- 5. CAUSES Lymphangitis is a type of secondary infection, which means it happens because of another infection. When the infection travels from the original site to the lymph vessels, the vessels become inflamed and infected. Bacterial infections are the most common cause of lymphangitis. Lymphangitis due to a viral or fungal infection is also possible. cytomegalovirus, tuberculosis, syphilis, and the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. Any injury that allows a virus, bacteria, or fungus to enter the body can cause an infection that leads to lymphangitis. Some possible culprits include: •puncture wounds, such as from stepping on a nail or other sharp object •untreated or severe skin infections, such as cellulitis •insect bites and stings •a wound that requires stitches •infected surgical wounds •sporotrichosis, a fungal skin infection common among gardeners Lymphangitis most often results from an acute streptococcal infection of the skin. Less often, it is caused by a staphylococcal infection. Lymphangitis may be a sign that a skin infection is getting worse. The bacteria can spread into the blood and cause life-threatening problems.
- 6. RISK FACTOR People with weak immune systems may be more vulnerable to lymphangitis. Having certain conditions, such as diabetes, HIV, or cancer, or taking drugs that suppress the immune system, including chemotherapy drugs, may all increase the risk of lymphangitis. •chronic steroid use •chickenpox
- 7. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY The major function of the lymphatic system is to resorb fluid and protein from tissues and extravascular spaces. The absence of a basement membrane beneath lymphatic endothelial cells affords the lymphatic channels a unique permeability, allowing resorption of proteins that are too large to be resorbed by venules. Lymphatic channels are situated in the deep dermis and subdermal tissues parallel to the veins and have a series of valves to ensure one-way flow . Lymph drains via afferent lymphatics to regional lymph nodes and then by efferent lymphatics to the cisterna chyli and the thoracic duct into the subclavian vein and venous circulation. Lymphangitis most commonly develops after cutaneous inoculation of microorganisms that invade the lymphatic vessels and spread toward the regional lymph nodes. Organisms may invade lymphatic vessels directly through a skin wound or an abrasion or as a complication of a distal infection.
- 8. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS People with lymphangitis may notice red streaks extending from the site of an injury to areas where there are a lot of lymph glands, such as the armpits or groin. Unexplained red streaks on any area of the body could also be a sign of lymphangitis, especially in a person who has an existing skin infection. Other symptoms of lymphangitis can include: •a recent wound that is not healing •feeling sick or weak •a fever •chills •a headache •low energy and loss of appetite •swelling near an injury or the groin or armpits
- 9. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS •Fever and chills •Enlarged and tender lymph nodes (glands) -- usually in the elbow, armpit, or groin •General ill feeling (malaise) •Headache •Loss of appetite •Muscle aches •Red streaks from the infected area to the armpit or groin (may be faint or obvious) •Throbbing pain along the affected area Lymphangitis can spread to the blood if left untreated. This life-threatening infection called sepsis may cause a very high fever, flu-like symptoms, and even organ failure. A person who feels very ill following an injury, or who has a high fever and symptoms of lymphangitis, should seek emergency medical attention
- 10. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION such as a biopsy to reveal the cause of the swelling or a blood culture to see if the infection is present in blood.
- 11. MANAGEMENT cephalosporins – cephalexin at a dose of 0.5 mg for between 7 and 10 days – or extended- spectrum penicillin. Methiciline-resistant staphylococcus aureus is common in communities and hence the need to use improved antibiotic drugs such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 7 to 10 days. Naficillin, oxacillin, and dicloxacillin are also effective against infections of the lymphatic system •pain medication •anti-inflammatory medication acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil). •surgery to drain any abscesses that may have formed •surgical debridement, or removal, of a node if it’s causing obstruction
- 12. MANAGEMENT aid healing and ease the pain by using a hot compress at home. Run hot water over a washcloth or towel and apply it to the tender area. Do this three times a day. The warmth will promote blood flow and encourage healing. For the same reason, you might also want to take warm showers, positioning the showerhead over the infected area. If possible, keep the infected area elevated. This helps reduce swelling and slows the spread of infection.